Unpacking Scope 3 Emissions: The Different Categories Explained
As we know Scope 3 pertains to all the indirect emissions that take place within a company's value chain. The 15 categories under scope 3 serve as a structured model for companies to quantify, oversee, and curtail emissions across their corporate value chain. These categories are exclusively formulated to prevent any possibility of the company accounting for emissions twice under multiple categories. Here you can learn briefly about the different categories and their definitions.
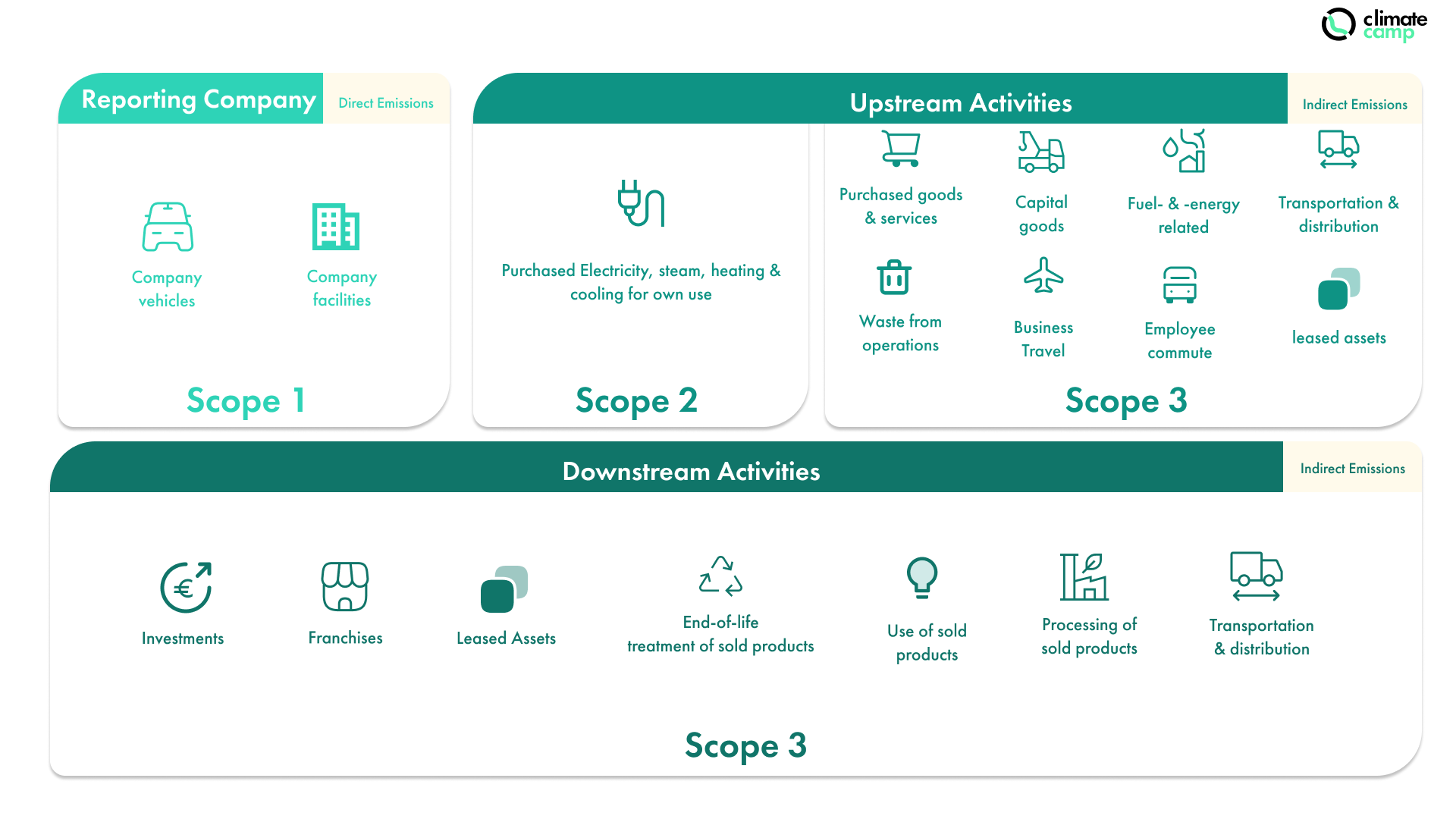
Upstream Activities
Upstream emissions are generated during the production of a company's goods or services

Category 1: Purchased Goods & Services
The procurement, manufacturing, and delivery of goods and services obtained by your organization during the reporting year that do not fall under any of the categories 2-8. This includes the extraction, production, and transportation of such goods and services that were acquired or purchased by your organization. Learn More
Category 2: Capital Goods
The emissions related to the manufacturing, extraction, or transportation of a product. That come from capital goods, which are physical assets, such as equipment, machinery, and buildings, that organizations use to produce goods or provide services. Within the organization's reporting year. Learn More
Category 3: Fuel- and energy-related activities (not included in Scope 1 or Scope 2)
The indirect GHG emissions resulting from fuel and energy-related activities that are not covered in Scope 1 or Scope 2. This category includes GHG emissions that occur outside your organization's own operations but are still associated with its activities or products. For instance, if a company's employees travel to work using personal vehicles, the GHG emissions associated with their transportation would be included in Category 3 emissions. Learn More
Category 4: Upstream transportation and distribution
The emissions associated with the movement and delivery of goods bought by your organization during the reporting year, between your organization's primary suppliers and its own operations using transportation and facilitates not owned or managed by your organization. This includes logistics, outbound logistics for sold products, as well as transportation and distribution between your organization's own facilities. These transportation and distribution services were procured by your organization during the reporting year. Learn More
Category 5: Waste generated in operations
Includes the GHG emissions associated with the use of a company's products or services, including emissions resulting from the energy used to operate or maintain those products. This can include emissions from the use of consumer goods, such as appliances or electronics, as well as emissions from the use of industrial equipment or machinery. For instance, if a company produces and sells air conditioners, the GHG emissions associated with the energy used to operate those air conditioners would be included in Category 5 emissions. Learn More
Category 6: Business travel
During the reporting year, your organization facilitated the transportation of its employees for business-related activities using vehicles that were neither owned nor operated by your organization. Learn More
Category 7: Employee Commuting
These emissions are those emitted during the reporting year, your organization facilitated the transportation of its employees between their homes and worksites using vehicles that were neither owned nor operated by your organization. Learn More
Category 8: Upstream leased assets
The lessee reported on the operation of assets leased by your organization during the reporting year that were not included in their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. Learn More
Downstream Activities
Downstream emissions occur during their usage and disposal.

Category 9: Downstream transportation and distribution
During the reporting year, your organization transported and distributed its products to end consumers, including retail and storage, using vehicles and facilities that were not owned or controlled and paid for by your organization. Learn More
Category 10: Processing of sold products
This category involves the processing of intermediate products sold by downstream organizations, such as manufacturers, during the reporting year. Learn More
Category 11: Use of sold products
The consumption of products and services sold by the reporting your organization during the reporting year. Learn More
Category 12: End-of-life treatment of sold products
The disposal and treatment of products sold by your organization at the end of their useful life during the reporting year. Learn More
Category 13: Downstream leased assets
The lessor reported (your organization) on the operation of assets you own and lease to other entities during the reporting year, which are not included in their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. Learn More
Category 14: Franchises
The franchisor reported on the operation of franchises that were not included in their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions during the reporting year. Learn More
Category 15: Investments
The operation of investments, such as equity and debt investments and project finance, that were not included in their Scope 1 or Scope 2 emissions during the reporting year. Learn More
In Conclusion
Scope 3 categories are an essential aspect of measuring an organization's environmental impact. While Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions are relatively easy to measure, Scope 3 emissions are often more complex and require a deep understanding of an organization's entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, and product end-of-life stages. The 15 categories outlined by the Greenhouse Gas Protocol provide a comprehensive framework for organizations to identify and measure their Scope 3 emissions, allowing them to make more informed decisions about sustainability initiatives and reduce their overall environmental impact. By considering Scope 3 emissions, organizations can enhance their sustainability efforts and build a more resilient and responsible business model for the future.